Today’s Focus of Attention is reader-supported. We sometimes include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission.
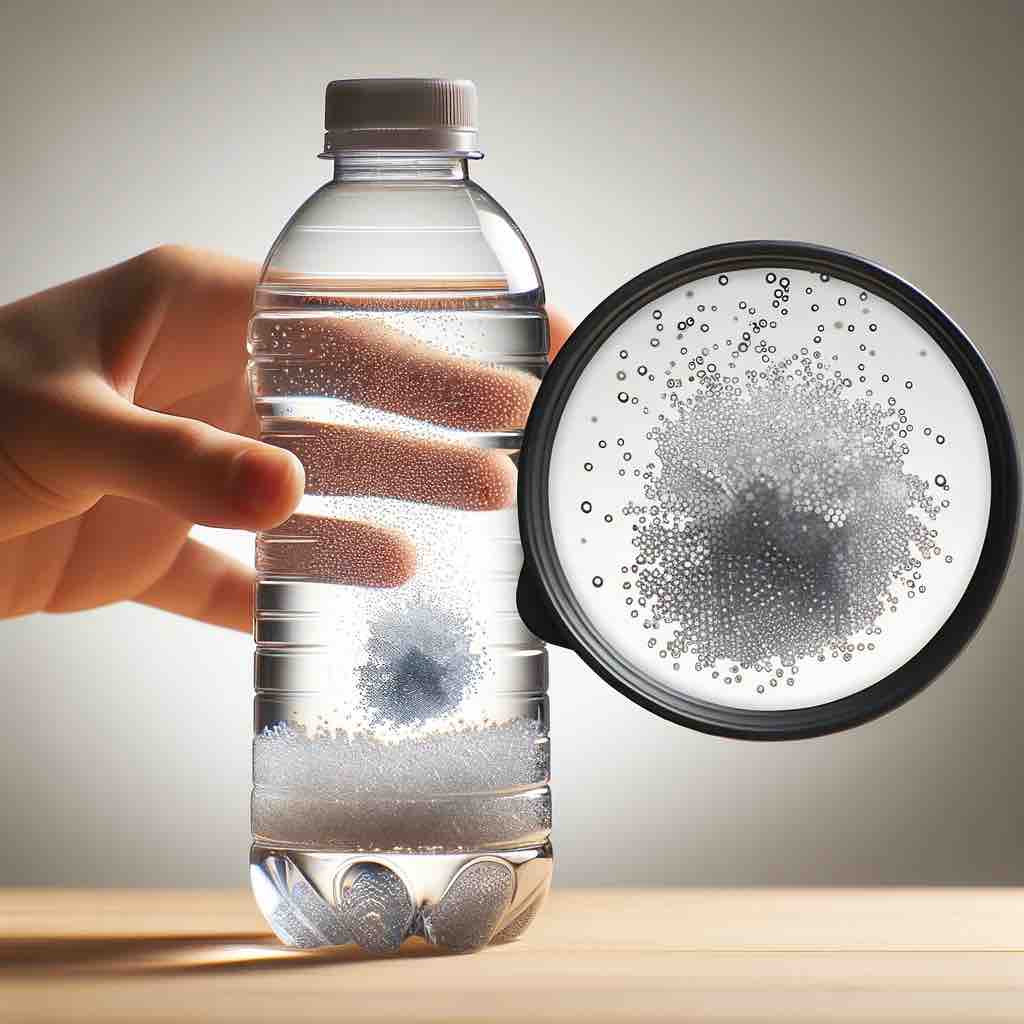
In new research, scientists from Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Laboratory have discovered hundreds of thousands of toxic, potential cancer-causing plastic nanoparticles in bottled water.
This suggests that every time you drink water from a disposable plastic bottle, you are poisoning your body.
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, nanoplastics are linked to fertility problems, birth defects, and even cancer, with an estimated 100,000 premature deaths in the US alone each year.
How Was It Discovered?
With the most sophisticated scanning technology, scientists from Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Laboratory analysed samples from three popular American brands and found an average of 240,000 plastic nanoparticles in a one-litre bottle of water.
The highest number detected was 370,000 particles.
Shockingly, tap water has only 5.5 per litre.
Researchers noted that those particles are so small that they can enter your cells and cross the blood-brain barrier. What was the most shocking part? The quantity proved to be 10 to 100 times greater than initially thought.
The investigation, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is more evidence of the harmful effects plastics have on humans.
Naixin Qian, the study’s lead author, said, “For a long time before this study, I actually thought that what was inside bottled water was just a few hundred PET particles.”
“It turns out to be more than that.”
Beizhan Yan, research co-author, stated that while plastic is not too toxic at a larger scale, its toxicity increases as it becomes smaller, as it can interfere in the cells, tissues, and organelles.
Yan showed no surprise to find such an amount of nanoplastics, since most water bottles are made of plastic.
One of the nanoplastics found in the study was polyethylene terephthalate (PET), also used in bottled sodas, sports drinks, and other products, including mayonnaise and ketchup.
But polyamide, a type of nylon, surpassed PET. Ironically, it may come from the plastic filters that ‘supposedly’ purify the water before filling the bottles.
What are Nanoplastics?
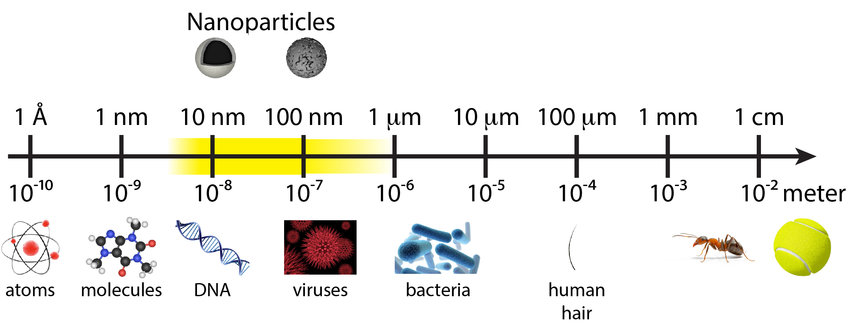
Nanoplastics are microscopic particles measuring less than 100 nanometres in size. They result from the breakdown of plastic debris, including water bottles and bags, and are present in every environment on our planet, both marine and terrestrial.
To put it in perspective, a nanometre is one billionth of a metre. Most proteins are 10 nanometres; a typical virus is 100; a bacterium is 1,000 and a human red blood cell is around 10,000 nanometres.
With common things, a sheet of paper is 100,000 nanometres; a strand of human DNA is 2.5; and an average atom is somewhere from 0.1 to 0.5 nanometres.
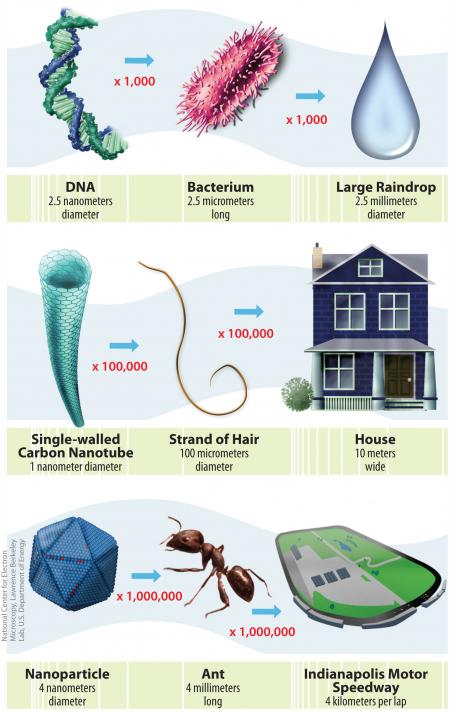
This scale gives us an idea of the size of nanoplastics and that, with such a minuscule form, they can enter anything in our body, from our bloodstream and lungs to our brains and cells.
Imagine the damage if those NPs accumulate in our bodies as time passes.
Microscopic Menaces
Polystyrene (PS) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are the most common types of plastics used in everyday products, such as bags, bottles, and food containers.
In recent years, most studies have focused on the impact of polystyrene nanoparticles (PS NPs) and have shown that they penetrate the cell membrane, accumulate, and incite an inflammatory response. However, the potential effects of PET NPs on biological organisms remain largely unstudied.
Plastics ‘do not biodegrade’; they break down into tinier fragments, which can stay in the environment for hundreds, if not thousands, of years.
Consider this every time you buy and dispose of a plastic bottle, food container, candy wrapper, or bag.
Had there been other studies?
In 2018, a study identified about 300 microplastic particles in a litre of bottled water. The conventional technique they used could show microplastics ranging from 5mm down to 1 micrometre (a millionth of a metre).
Back then, researchers didn’t have the technology to find smaller particles. Now they can. Nanoplastics are less than 1 micrometre, so in those days, it was impossible to identify them.
Final Thoughts
Plastic production continues to grow and is expected to keep going that way.
Over 30 million tonnes are dumped every single year in the oceans, rivers, lakes, and land. And all of them are breaking down into smaller and smaller particles until they reach the nanoscale.
Bottom line: we are choking ourselves with plastics, and we know nothing about their toxicity in the long run.
Doctors have even found plastics in the lungs of patients, so are we waiting to have them in our brains too and see how they affect our cognitive function? Am I exaggerating? I think not.
What are our options? Well, the first thing is not to buy plastic bottles and stop using single-use plastics. Is it hard? Of course, but what else can we do? This action is for our own health, and neither governments nor companies will do anything to save us.
We’d like to hear from you. Please share your comments.


